Abstract
Introduction Immunoglobulin heavy-chain variable genes (IGHV) is critical for the defining epitope binding affinityand B cell differentiation. Lymphoplasmacytic lymphoma/Waldenström macroglobulinemia (LPL/WM) is a heterogeneous diseasewhose role of IGHV usage remains unknown. Besides, the clinical relevance of IGHV repertoire for LPL/WM remain largely unexplored. The aim of our study is to explore the IGH repertoire of LPL/WM in by far the largest series, and to evaluate the correlation between IGH rearrangements and genetic aberrations and clinical characteristics of LPL/WM patients.
Methods A total of 162 patients with a diagnosis of LPL/WM were included in this study. Polymerase chain reaction (PCR)amplification of IGHV-IGHD-IGHJ was performed on genomic DNA or cDNA samples using the IGH Somatic Hypermutation Assay v2.0 (Invivoscribe, Technologies, San Diego, US). Sequences were aligned to IMGT (http://www.imgt.org/IMGT_vquest/vquest) and IGBLAST (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/igblast/) databases. IGH gene repertoires, mutation status, IGHV CDR3 characteristics, genetic aberrations, MYD88 mutation status and clinical characteristics were collected to evaluate the relevance.
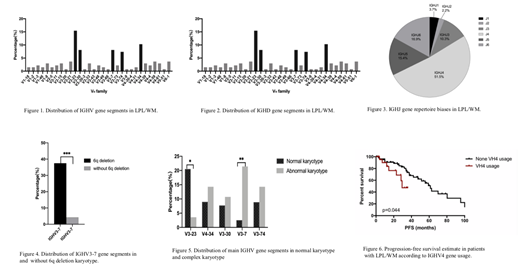
Results Productive IGHV-D-J rearrangements were obtained in 136 out of 162 patients (84.0%). The IGHV gene repertoire was remarkably biased in LPL/WM. IGHV3-23 (15.4%), IGHV4-34 (10.3%), IGHV3-7 (8.1%), IGHV3-30 (7.4%) and IGHV3-74 (7.4%) were significantly overrepresented in LPL/WM(Figure 1). Among the 134 IGHD data, the most frequent segment was IGHD3-10 (21/134, 15.7%), followed by IGHD6-13 (18/134, 13.4%) (Figure 2). Among the 134 IGHJ data, IGHJ4 segment was selected in more than half of these rearrangements (70/136; 51.5%), followed by IGHJ6 (23/136; 16.9%) and IGHJ5 (21/136; 15.4%) (Figure 3). Most of the cases were mutated (97.0%) using a 98% IGHV germline homology cutoff. IGHV3-30 was associated with long heavy chain CDR3, indicating the specific antigen selection in LPL/WM. Patients with IGHV3-7 were significantly more likely to harbor 6q deletion (p<0.001)(Figure 4) and abnormal karyotype (p=0.004)(Figure 5).The IGHV hypermutation rate in patients with MYD88 L265P mutation was significantly higher than in wild-type patients (7.3% vs5.6%, p=0.009). IGHV3-23 and IGHV3-74 segments were more frequently detected in MYD88 mutated LPL/WM patients (25.7% vs. 4.3%, p=0.025). IGHV3-7 and IGHV4-59 were represented more in MYD88 wildtype patients (30.4% vs. 8.9%,p=0.005). Moreover, Patients with IGHV4 especially IGHV4-34 had higher level of LDH. IGHV4 was a prognostic marker of shorter progression-free-survival (Figure 6).
Conclusion LPL/WM appears to be composed ofdifferent subgroups based on the IGHV repertoire. The mutational status and the IGHV CDR3 length indicated the role for antigenselection in LPL/WM development. The presence of IGHV4 genes proved to be a potential risk factor associated with outcome which deserved further study.These results showed for the first time that IGHV repertoire had clinical relevance in LPL/WM.
Wang: AbbVie: Consultancy; Astellas Pharma, Inc.: Research Funding.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal